The new NIH Public Access Policy has been in effect for a couple of months, requiring that NIH-funded research be made available in PubMed Central immediately upon acceptance for publication.
How can you comply?
Our library guide walks you through some of the key steps you need to do as an author, from strategically selecting where to publish, publisher-specific policies, and when and how to deposit the author-accepted manuscript. In addition, a recent webinar from the University of Nevada, Reno’s Savitt Medical Library highlighted some of the details of this policy change:
- The new policy applies to “manuscripts accepted for publication in a journal, on or after July 1, 2025.” Compliance will be tracked through My Bibliography based on the earliest publication date in PubMed.
- If the published work is based on a grant that ended before July 1, 2025, it is not subject to the updated policy.
- Neither publishing open access nor posting your manuscript to a preprint server counts as compliance.
The webinar and our guide offer useful advice that may help you select a journal to target for publication:
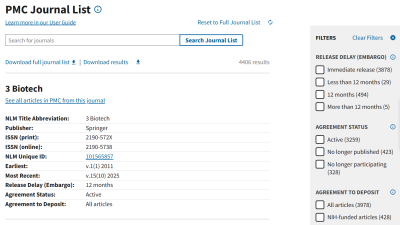
- The PMC journal list includes key information from journals that currently or previously agreed to deposit the final published version of NIH-funded articles directly to PMC. You can search for journals based on their agreement status and embargo period.
- The agreement status remains the most up-to-date piece of information listed. If a journal is listed as “no longer participating,” no further articles are being deposited into PMC, regardless of previous agreements.
- After searching the PMC journal list, visiting our frequently updated publisher policy list, or viewing the website of the journal in question, reaching out to the journal to confirm the policy in writing remains a best practice.
Still have questions? Reach out to the Library and we will do our best to advise you.