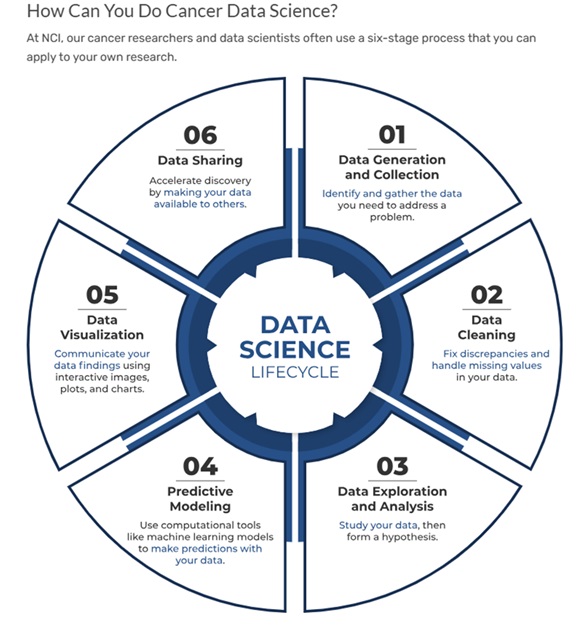
With data sharing increasingly being encouraged in academic research and datasets increasingly being added to data repositories and being published on the Web, it makes sense that a Web browser company like Google would dedicate resources towards the goal of developing a Web discovery tool that is optimized for finding datasets.
How does it work?
Google Dataset Search, a dataset-discovery tool, basically uses Google’s web crawl technology to search for datasets that have been made available on the Web, identifying them based on their metadata (standardized descriptions of the datasets added to them by their owners/publishers).“ Google’s Dataset Search extracts dataset metadata—expressed using schema.org and similar vocabularies—from Web pages in order to make datasets discoverable.”
For an in-depth overview of how Google Dataset Search has been developed – please see:
Sostek, Katrina, Daniel M. Russell, Nitesh Goyal, Tarfah Alrashed, Stella Dugall, and Natasha Noy. “Discovering datasets on the web scale: Challenges and recommendations for Google Dataset Search.” Harvard Data Science Review Special Issue 4 (2024).
How can you search it?
To get started with using Google Dataset Search, go to: Dataset Search at https://datasetsearch.research.google.com/
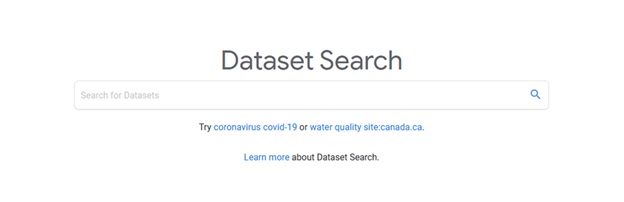
If you are looking for something specific, you can refine your search results by limiting your search to a particular website domain (for example, site:nih.gov) or adding additional terms to your search. You can also filter your results by when the dataset was last updated, by format, by usage rights, topic/discipline, and whether the dataset is freely-available. Furthermore, you can save your search results, link-out to the external source website where you can download the datasets, and you can easily cite the dataset by copying the citation information that is generated when you click on the citation button (i.e. the quotation mark button).
To learn more – see:
Dataset Search Quick Start Guide –
https://newsinitiative.withgoogle.com/resources/trainings/dataset-search-quickstart-guide/
User Support Center – https://datasetsearch.research.google.com/help
Dataset Developer Page –
https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/structured-data/dataset
How is it being used?
It appears that biomedical researchers have already started using Google Dataset Search in their scholarly projects. Some examples focusing on finding image datasets include:
- Abbad Andaloussi M, Maser R, Hertel F, Lamoline F, Husch AD. Exploring adult glioma through MRI: A review of publicly available datasets to guide efficient image analysis. Neurooncol Adv. 2025;7(1):vdae197. Epub 20250128. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdae197. PubMed PMID: 39877749; PMCID: PMC11773385.
- Rozhyna A, Somfai GM, Atzori M, DeBuc DC, Saad A, Zoellin J, Müller H. Exploring Publicly Accessible Optical Coherence Tomography Datasets: A Comprehensive Overview. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14(15). Epub 20240801. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151668. PubMed PMID: 39125544; PMCID: PMC11312046.
- Wen D, Khan SM, Ji Xu A, Ibrahim H, Smith L, Caballero J, Zepeda L, de Blas Perez C, Denniston AK, Liu X, Matin RN. Characteristics of publicly available skin cancer image datasets: a systematic review. Lancet Digit Health. 2022;4(1):e64-e74. Epub 20211109. doi: 10.1016/s2589-7500(21)00252-1. PubMed PMID: 34772649.
- Khan SM, Liu X, Nath S, Korot E, Faes L, Wagner SK, Keane PA, Sebire NJ, Burton MJ, Denniston AK. A global review of publicly available datasets for ophthalmological imaging: barriers to access, usability, and generalisability. Lancet Digit Health. 2021;3(1):e51-e66. Epub 20201001. doi: 10.1016/s2589-7500(20)30240-5. PubMed PMID: 33735069.
Questions? Ask Us at the MSK Library!