With the launch of ResearchKit, Apple has turned the iPhone into a medical research tool. ResearchKit makes it possible to generate large, wide-ranging datasets about the day-to-day of disease. Additionally, it allows researchers to recruit participants for large-scale studies. Bloomberg Business reported that 11,000 people had signed up for a cardiovascular study at Stanford University 24 hours after ResearchKit was introduced. Researchers at UCLA have already developed an app with ResearchKit for breast cancer, called Share the Journey: Mind, Body and Wellness after Breast Cancer – this app builds on the work of applied mathematician and TED Fellow Max Little. If you’re interested in finding out more about how Max Little’s work influenced the development of ResearchKit, you can watch his TED talk from 2012: A test for Parkinson’s with a phone call.
Category Archives: Tech Zone
Liquid Biopsy Breakthrough for Early Stage Cancer Detection
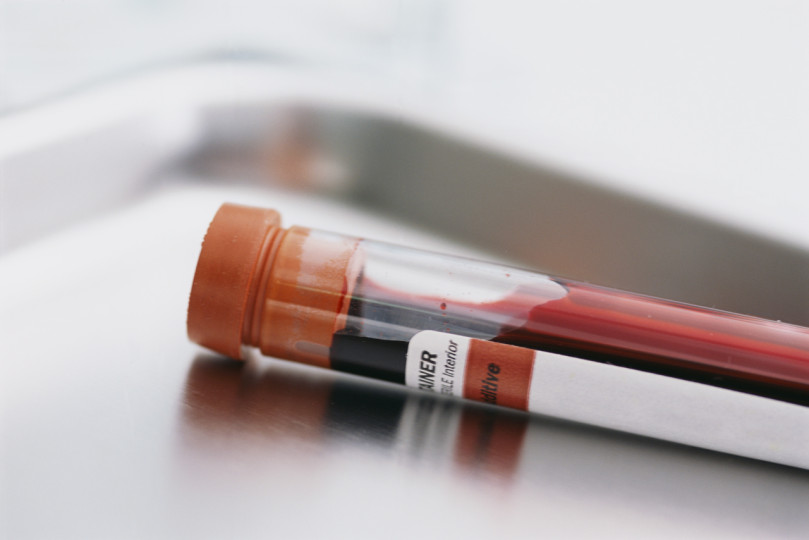 Professor Dennis Yuk Ming Lo, associate dean of medicine at Chinese University, has developed a new method called liquid biopsy, which he claims can detect many kinds of cancer at a very early stage. Lo’s method decodes millions of DNA fragments in a human’s blood with the use of a DNA-sequencing machine. The results are then compared to that of a normal human genome or a complete set of human DNA. Researchers can now spot rearranged DNA patterns – a significant sign of a tumor. The liquid biopsy technology, cited by MIT Technology Review, is the result of over 20 years of research.
Professor Dennis Yuk Ming Lo, associate dean of medicine at Chinese University, has developed a new method called liquid biopsy, which he claims can detect many kinds of cancer at a very early stage. Lo’s method decodes millions of DNA fragments in a human’s blood with the use of a DNA-sequencing machine. The results are then compared to that of a normal human genome or a complete set of human DNA. Researchers can now spot rearranged DNA patterns – a significant sign of a tumor. The liquid biopsy technology, cited by MIT Technology Review, is the result of over 20 years of research.
Magnetic Nanoparticles Could Stop Blood Clot-Caused Strokes
 Researchers have found that loading magnetic nanoparticles, to deliver the clot-busting drug tPA (tissue plasminogen activator), offers a much more efficient journey, promising to destroy blood clots 100 to 1,000 times faster and aid significantly in the prevention of heart attacks and strokes.
Researchers have found that loading magnetic nanoparticles, to deliver the clot-busting drug tPA (tissue plasminogen activator), offers a much more efficient journey, promising to destroy blood clots 100 to 1,000 times faster and aid significantly in the prevention of heart attacks and strokes.
Read the Newswise press release for more details about the findings. The research paper is available online:
Voros et al. TPA Immobilization on Iron Oxide Nanocubes and Localized Magnetic Hyperthermia Accelerate Blood Clot Lysis. Adv Funct Mater. 2015 Feb 11. [early view]