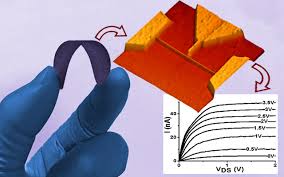
 Researchers from the Martinez Research Group in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Purdue University have shown how standard inkjet-printers can be employed to produce flexible electronic circuits from liquid-metal nanoparticle inks. These elastic technologies could revolutionize medicine by making possible a new class of pliable robots and stretchable garments that people might wear for therapeutic purposes. Read more about the research recently published in Advance Materials.
Researchers from the Martinez Research Group in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Purdue University have shown how standard inkjet-printers can be employed to produce flexible electronic circuits from liquid-metal nanoparticle inks. These elastic technologies could revolutionize medicine by making possible a new class of pliable robots and stretchable garments that people might wear for therapeutic purposes. Read more about the research recently published in Advance Materials.